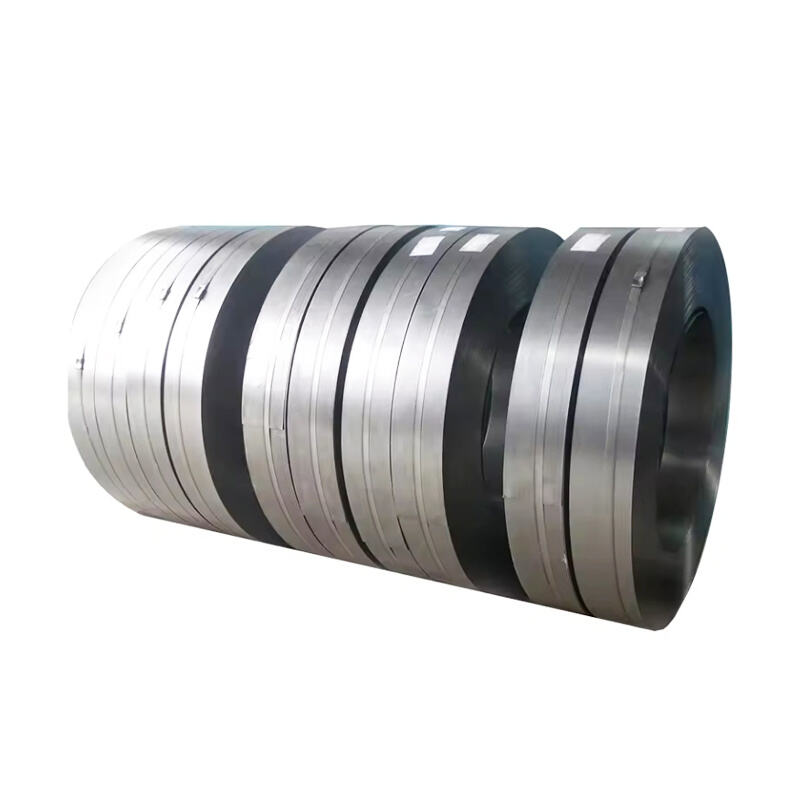
silicon steel uses
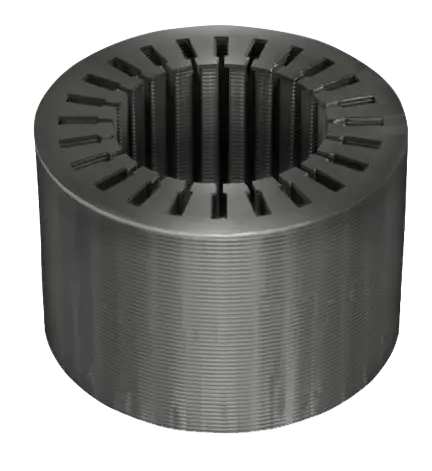
Silicon steel, also known as electrical steel or transformer steel, plays a pivotal role in modern electrical applications. This specialized material combines iron with silicon content ranging from 0.5% to 3.25% to create a magnetic material with exceptional electromagnetic properties. The primary function of silicon steel is to enhance magnetic permeability while reducing core losses in electrical equipment. Its unique crystalline structure allows for efficient magnetic flux distribution, making it essential in transformers, motors, and generators. The material's low hysteresis loss and high magnetic permeability enable efficient energy transfer, while its resistance to magnetic aging ensures long-term stability. Silicon steel comes in two main varieties: grain-oriented (GO) and non-oriented (NO), each optimized for specific applications. GO silicon steel is particularly valuable in transformers due to its superior magnetic properties in the rolling direction, while NO silicon steel finds extensive use in rotating machinery. The material's technological features include carefully controlled grain size, precise silicon content, and specialized surface coatings that minimize energy losses and improve insulation properties. These characteristics make silicon steel indispensable in power generation, distribution systems, and various electrical devices that require efficient magnetic core materials.